Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids: Understanding Their Effects, Benefits, Risks, And Legal Status For Medical Use
Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds found in cannabis plants. While THC is the most well-known cannabinoid, there are over 100 others that have been identified. Cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a network of receptors that play a role in regulating a variety of bodily functions, including pain, inflammation, mood, and sleep.
Potential health benefits of cannabinoids
Cannabinoids have been shown to have a wide range of potential health benefits, including:
- Pain relief: Cannabinoids have been shown to be effective in relieving pain from a variety of conditions, including chronic pain, arthritis pain, and cancer pain.
- Inflammation reduction: Cannabinoids have anti-inflammatory properties, making them potentially beneficial for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Anxiety relief: Cannabinoids have been shown to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Sleep improvement: Cannabinoids can help to improve sleep quality and duration.
- Neuroprotection: Cannabinoids have neuroprotective properties, meaning they may help to protect the brain from damage.
Lesser-known cannabinoids with medical benefits
In addition to THC and CBD, other cannabinoids that offer medical benefits include:
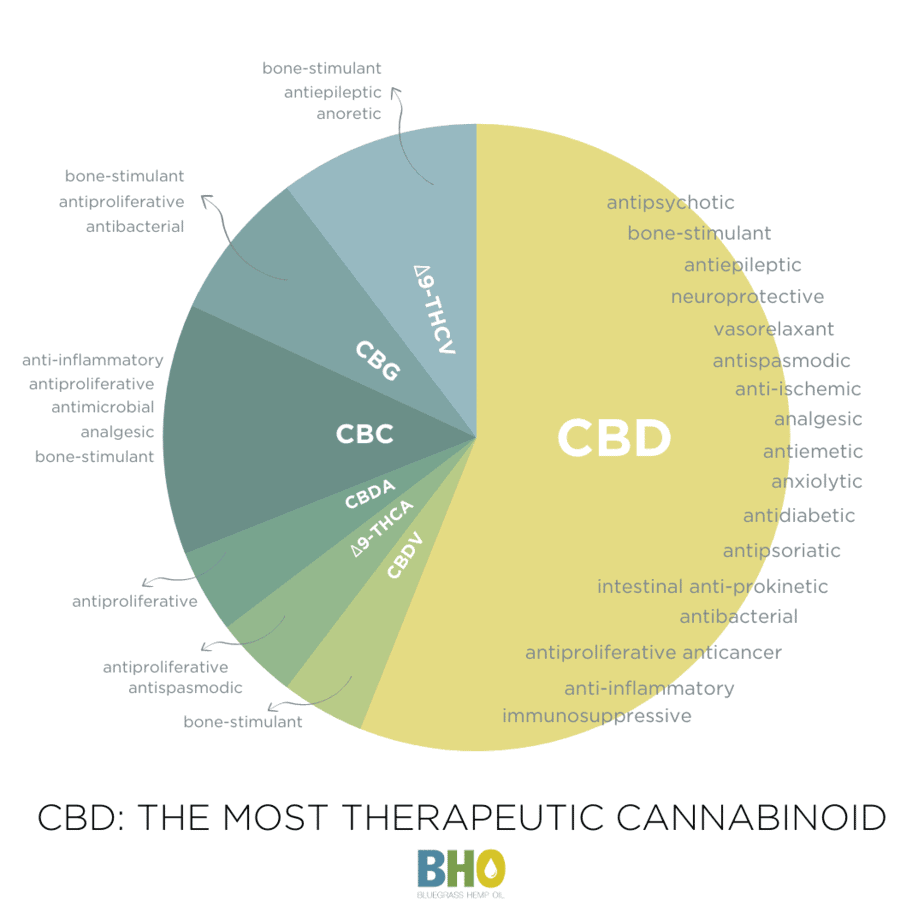
- CBC (cannabichromene): CBC has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It is also being studied for its potential to treat cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
- CBG (cannabigerol): CBG has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and analgesic properties. It is also being studied for its potential to treat cancer and glaucoma.
- CBN (cannabinol): CBN has sedative and analgesic properties. It is also being studied for its potential to treat insomnia and pain.
Risks and legal status of cannabinoids
While cannabinoids are generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential side effects, such as drowsiness, dry mouth, and anxiety. It is important to start with a low dose and increase gradually to avoid any side effects.
The legal status of cannabinoids varies from country to country. In the United States, CBD is legal at the federal level, but THC is still classified as a Schedule I controlled substance.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about cannabinoids so that you can make informed decisions regarding your health and wellness journey.
Key Takeaways
- Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis plants that can treat many ailments and diseases by interacting with human brain and body receptors.
- CBD is a famous non-psychoactive cannabinoid with potential health benefits, while THC is responsible for causing marijuana’s psychoactive effects.
- There are over 100 different types of cannabinoids found in cannabis, each with unique properties and potential therapeutic effects, such as anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and analgesic properties.
- It is essential to purchase CBD products from reputable companies that test their products for quality and safety and to consult a healthcare provider before taking cannabinoids, as they can interact with other medications and supplements.
What are cannabinoids, and how do they work in the body?
Cannabinoid Therapy: A Promising Approach to Holistic Wellness
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis plants that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a wide range of therapeutic effects. The endocannabinoid system is a network of receptors that play a vital role in regulating many bodily functions, including sleep, appetite, pain, and immune response.
Cannabinoids bind to these receptors to trigger different physiological responses, making them a promising approach to holistic wellness. Cannabinoid therapy involves using cannabinoids to treat a variety of medical conditions, including chronic pain, inflammation, anxiety, and insomnia.
Finding the right dosage
Finding the right dosage of cannabinoids is essential for optimal therapeutic effects. The appropriate dosage depends on various factors, such as your weight, metabolism, and the severity of your condition. It is important to start with a low dose and increase gradually to avoid any adverse reactions.
Therefore, it’s essential to work with a healthcare provider experienced in cannabinoid therapy to determine the proper dosing for your needs.
Understanding how cannabinoids work in the body is crucial for anyone interested in exploring their potential benefits for health issues. Now that you know about cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system’s role in regulating vital functions, let’s dive into what makes each type of cannabinoid unique and how they affect our bodies differently.
What are the different types of cannabinoids, and what are their personal effects?
Cannabinoids: The Future of Natural Medicine?
Cannabinoids are quickly gaining attention as a new frontier in natural medicine. With their wide range of therapeutic potential, cannabinoids offer hope for people suffering from a variety of health conditions, including insomnia, inflammation, pain, anxiety, and depression.
One of the most exciting things about cannabinoids is that they are relatively safe and well-tolerated. Unlike many conventional medications, cannabinoids have few side effects and are not addictive.
Another advantage of cannabinoids is that they can be used in a variety of ways. Cannabinoids can be taken orally, vaporized, or applied topically. This makes it easy to find a delivery method that works best for you.
If you’re looking for a natural way to improve your health and well-being, cannabinoids may be worth exploring. Talk to your doctor about whether cannabinoid therapy is right for you and how to get started.
Cannabinoids: A Spectrum of Therapeutic Possibilities
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis plants that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a wide range of therapeutic effects. Each cannabinoid has its unique properties and benefits, offering new possibilities for treating various health issues.
Here is a brief overview of four lesser-known cannabinoids and their therapeutic potential:
-
CBN (cannabinol): CBN is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is primarily used for treating insomnia. It has sedative and hypnotic effects that can help promote relaxation and sleep. CBN may also be helpful in reducing pain and inflammation.
-
CBC (cannabichromene): CBC has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, making it useful in reducing inflammation and pain. It may also be helpful in treating inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, and other chronic pain conditions. CBC may also boost the immune system and protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
-
THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin): THCV is a psychoactive cannabinoid that has appetite-suppressing and metabolism-boosting effects. This makes it a potential treatment for obesity and other metabolic disorders. THCV may also be helpful in reducing anxiety and improving cognitive function.
-
CBG (cannabigerol): CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that has pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties. It may also be helpful in treating anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. CBG may also have neuroprotective effects and protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
In addition to these cannabinoids, there are cannabinoid acids that act as natural mood stabilizers. The most abundant cannabinoid acids found in cannabis are THCA and CBDA. CBDA has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it a potential anxiolytic and analgesic agent. Combining CBDA with other cannabinoids can create an entourage effect that offers more balanced and therapeutic effects.
Understanding the individual effects of each cannabinoid can help you determine which ones might be most beneficial for your specific needs. But first, you need to understand the difference between THC and CBD – which we’ll cover next.
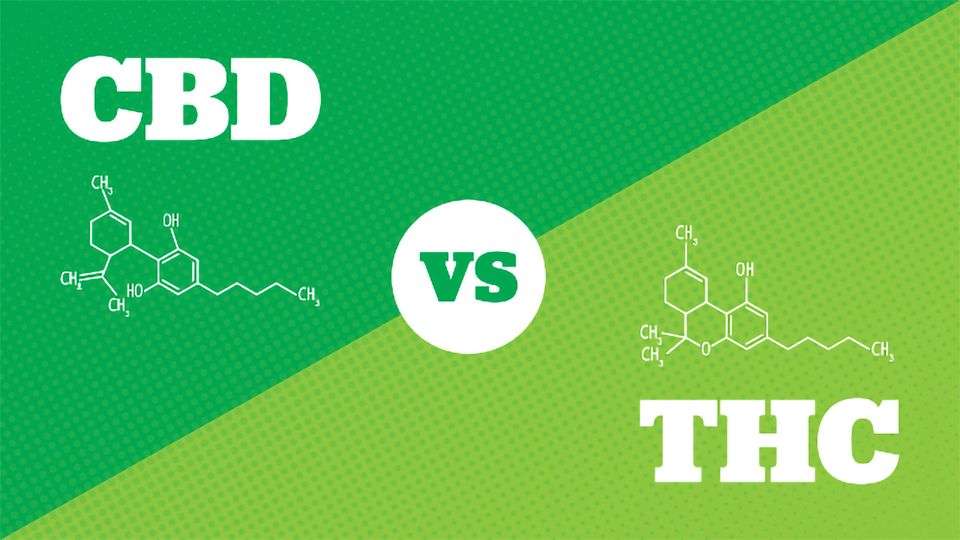
What is the difference between THC and CBD?
Imagine walking through a cannabis field and noticing the difference between the bright green leaves of CBD-dominant plants and the rich purple hues of THC-dominant ones. These two compounds are among the most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis and have different effects on health.
While THC is responsible for causing marijuana’s psychoactive effects, CBD is non-psychoactive and offers potential health benefits without altering one’s state of mind. THC and CBD interact with cannabinoid receptors in our bodies but produce different effects.
THC has been shown to reduce nausea, increase appetite, relieve pain, and induce euphoria or relaxation. In contrast, CBD may help reduce pain, inflammation, swelling, anxiety symptoms, seizures, and more. It’s important to note that there are dosage guidelines for THC and CBD, as taking too much can lead to potential risks such as impaired coordination or cognitive function.
The legal status of using cannabinoids varies depending on where you live. Some countries have legalized medical marijuana, while others have not. In the United States, marijuana is still classified as a Schedule I drug by the federal government despite being legal for medical use in many states. However, hemp-derived CBD products containing less than 0.3% THC are permitted at the nationallycertain conditions.
As with any substance used for medicinal purposes, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment plan involving cannabinoids. What are the potential medical benefits of using cannabinoids? Let’s explore this topic further.
What are the potential medical benefits of using cannabinoids?
Get ready to discover the incredible healing potential of these natural compounds that could positively impact your well-being. Cannabinoids, including CBD and THC, have been shown to offer various medical benefits.
For instance, they can reduce seizures, alleviate pain, and relieve anxiety. Additionally, cannabinoids possess anti-inflammatory effects that can help treat different health issues.
CBD has become extremely popular due to its therapeutic potential without causing psychoactive effects. It’s used for treating chronic pain management because it interacts with the endocannabinoid system in our body and reduces inflammation. Moreover, research indicates that CBD may be an effective treatment for anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder (SAD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and general anxiety disorder (GAD).
Furthermore, evidence suggests that cannabinoids may have potential cancer treatment properties. Cannabinoids offer promising therapeutic possibilities for various health issues, from reducing seizures to treating cancer. They are known for their anti-inflammatory effects, making them helpful in managing chronic pain conditions such as arthritis or multiple sclerosis. Additionally, they have shown promising resurelievingef from anxiety-related disorders like PTSD or GAD.
However, before incorporating any cannabinoid product into your routine, consult with a healthcare provider because there may be associated risks or side effects with using these natural compounds.
Are there any side effects or risks associated with using cannabinoids?
You may experience some side effects or risks when using cannabinoids, so it’s essential to be aware of potential issues before incorporating them into your wellness routine. While CBD is generally considered safe and non-addictive, some people may experience side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness, and changes in appetite or mood.
THC, on the other hand, can cause psychoactive effects and impair driving ability. It’s also important to note that specific populations may be more at risk for adverse side effects from cannabinoids. Pregnant women should avoid using cannabis products due to potential harm to fetal development. Individuals with a history of mental health disorders or addiction should consult a healthcare provider before using cannabinoids, as they may exacerbate these conditions.
Cannabinoids can interact with other medications and supplements, so you must inform your healthcare provider if you plan on using them. Some studies have suggested that CBD can affect how the liver metabolizes certain drugs, potentially leading to adverse reactions. Additionally, while rare, there is a potential for addiction with prolonged use of THC-containing products. It’s esseYou mustvariouse potential benefits against any risks before incorporating cannabinoids into your wellness routine.
As you consider incorporating cannabinoids into your wellness routine, it’s essential to understand their extraction and manufacturing process for medical use.
How are cannabinoids extracted and manufactured for medical use?
Like alchemists of old, modern manufacturers extract cannabinoids from the cannabis plant using various methods to create medical products that offer new therapeutic possibilities for various health issues.
The process begins with selecting high-quality cannabis plants and extracting the desired cannabinoids through different methods, such as solvent extraction and lipid-based extraction.
Quality control measures are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of cannabinoid-based medicines.
As manufacturers, we adhere to strict regulatory requirements for manufacturing processes and product testing. Quality control includes testing for potency, purity, and contaminants such as pesticides and heavy metals and ensuring consistency between batches.
Technological advancements in cannabinoid extraction methods may lead to even more precise dosing. Understanding how cannabinoids are extracted and manufactured is crucial for patients seeking cannabinoid-based therapies.
Purchasing these products from reputable companies that follow rigorous quality control protocols is essential. In the next section about the legal status of cannabinoids in different countries, you’ll learn how regulatory frameworks impact access to medical cannabis products worldwide.


What is the legal status of cannabinoids in different countries?
So, what’s the deal with cannabis and its legality worldwide? The legal implications of using cannabinoids vary greatly depending on where you are.
While some countries, such as Canada and Uruguay, have legalized cannabis for medicinal and recreational use, others still consider it a controlled substance. In many places where it is not fully legalized, there may be varying degrees of medical accessibility or societal acceptance.
Global regulations regarding cannabinoids continue to evolve as new research emerges about their potential benefits and risks. Culturally, different societies view cannabis use differently, impacting its legality. Despite progress towards legalization in some regions of the world, there are still concerns about addiction potential and other adverse health outcomes associated with its use.
While cannabinoids offer exciting possibilities for treating various medical conditions, navigating their legal status can be complex. It’s essential to understand the laws surrounding cannabis use in your area before trying to access any products containing cannabinoids.
As we move into a future where more research is conducted on these compounds, and societal attitudes shift towards greater acceptance of their use, it’ll be interesting to see how global regulations continue to change.
As you move forward learning about cannabinoids’ impact on your health and their interactions with other medications or supplements you may take regularly, understanding their legal status around the world provides an essential context for safe consumption. So let’s explore further how cannabinoids interact with other medications.
How do cannabinoids interact with other medications?
Get ready to discover how cannabinoids interact with your brain and nervous system, shaping how you experience pain, pleasure, and emotions.
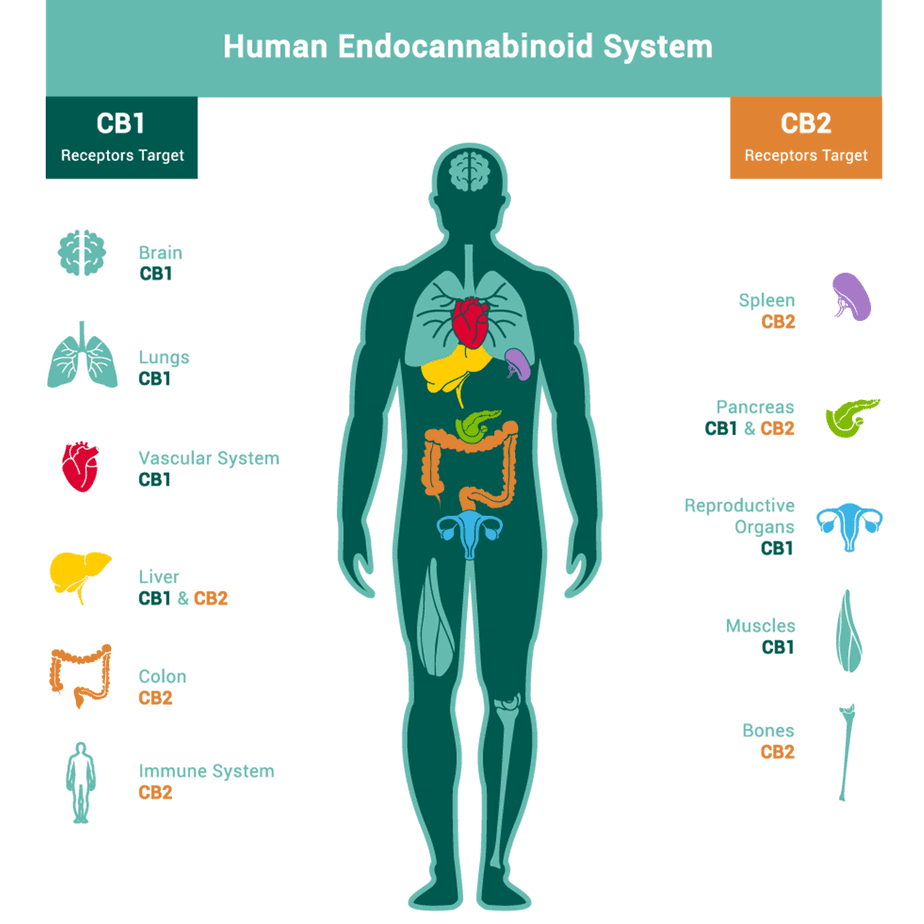
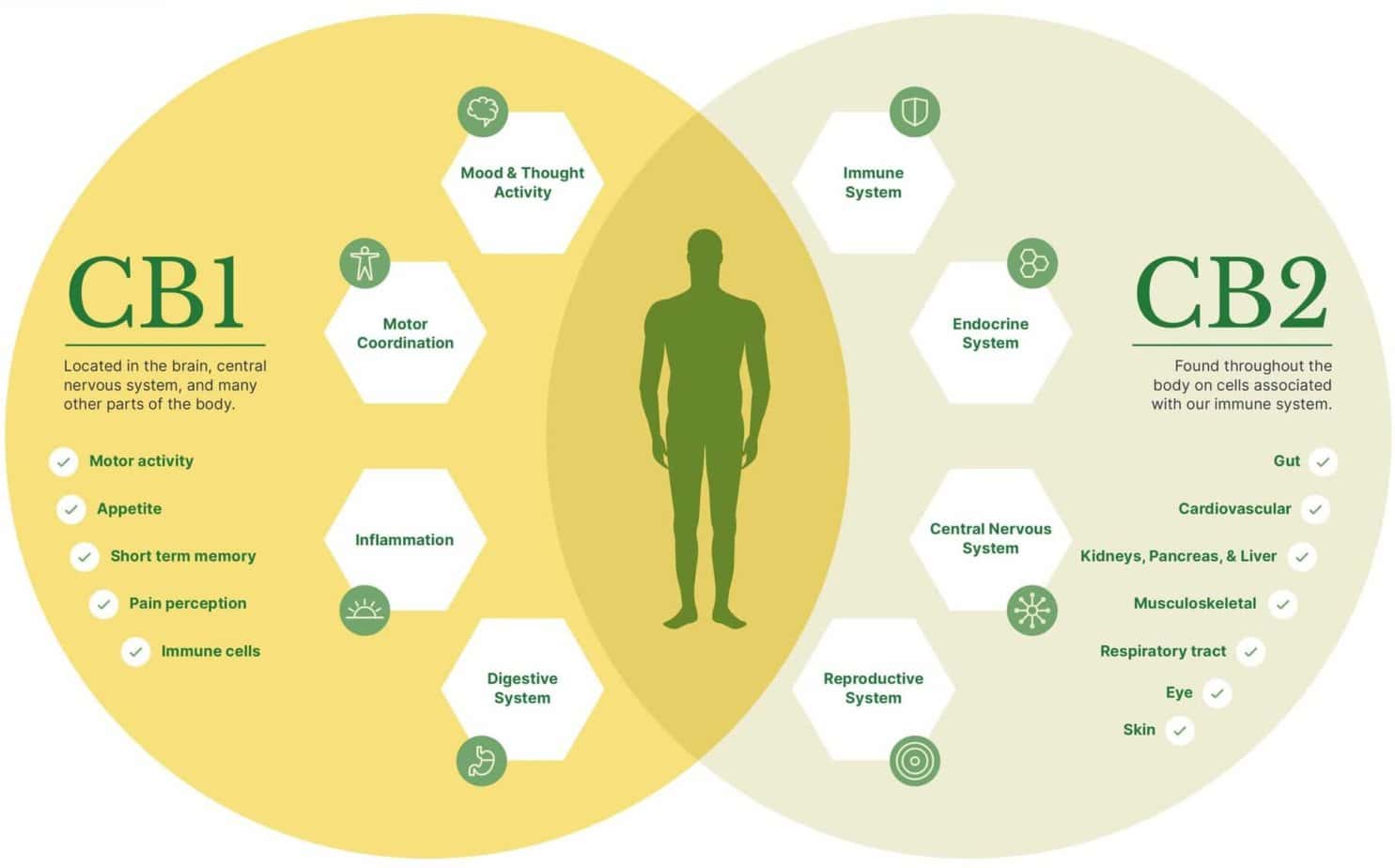
Cannabinoids bind to specific receptors in your body’s endocannabinoid system, which is crucial in regulating many physiological processes such as mood, appetite, sleep, and pain. The two primary cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2, with CB1 being mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 located mainly in immune cells.
The neurological effects of cannabinoids can vary depending on their concentration and the method of ingestion. THC can cause psychoactive effects by binding firmly to CB1 receptors in various brain parts associated with memory formation, decision-making skills, psychomotor performance, and cognitive function. On the other hand, CBD does not have a significant affinity for these receptors but acts indirectly by inhibiting enzymes that break down anandamide – an endocannabinoid that helps regulate mood.
Now that you know how cannabinoids affect your brain and nervous system, let’s explore if there are any long-term effects of using them.
How do cannabinoids affect the brain and nervous system?
Get ready to discover how cannabinoids interact with your brain and nervous system, shaping how you experience pain, pleasure, and emotions.
Cannabinoids bind to specific receptors in your body’s endocannabinoid system, which is crucial in regulating many physiological processes such as mood, appetite, sleep, and pain. The two primary cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2, with CB1 being mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 located mainly in immune cells.
The neurological effects of cannabinoids can vary depending on their concentration and the method of ingestion. THC can cause psychoactive effects by binding firmly to CB1 receptors in various brain parts associated with memory formation, decision-making skills, psychomotor performance, and cognitive function. On the other hand, CBD does not have a significant affinity for these receptors but acts indirectly by inhibiting enzymes that break down anandamide – an endocannabinoid that helps regulate mood.
Now that you know how cannabinoids affect your brain and nervous system, let’s explore if there are any long-term effects of using them.
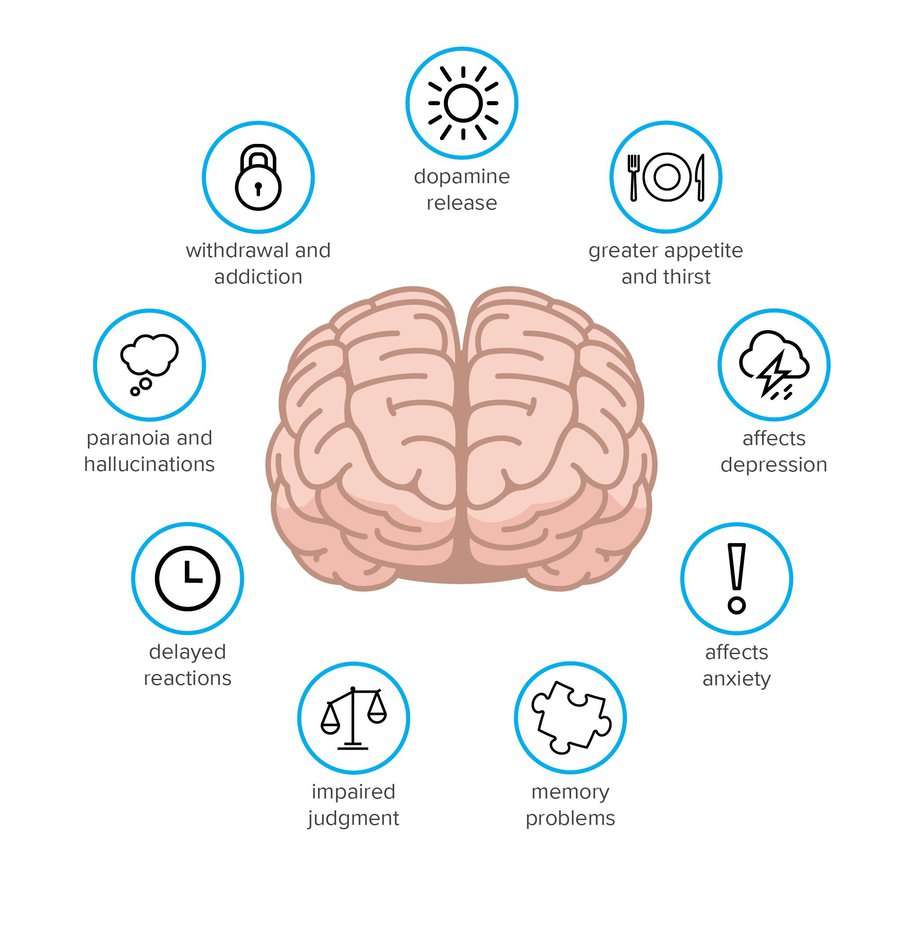
Are there any long-term effects of using cannabinoids?
Have you ever wondered if using cannabinoids, like cannabis, long-term could negatively affect your health? It’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with prolonged use.
One primary concern is the impact on cognitive function. Studies have shown that long-term use of cannabis can lead to memory impairment and decreased attention span.
Another risk associated with prolonged cannabinoid use is addiction potential. While not everyone who uses cannabinoids will become addicted, it’s essential to be aware that it can happen. One study found that 9% of people who used cannabis became dependent on it. Symptoms of withdrawal can include irritability, anxiety, and insomnia.
In addition to these risks, there are concerns about the impact on respiratory and cardiovascular health. Smoking cannabis can cause damage to lung tissue and increase the risk of respiratory infections. It may also increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for those with pre-existing heart conditions.
With all this in mind, weighing the potential benefits against these risks is crucial before deciding whether to use cannabinoids long-term. As you consider using cannabinoids for medical purposes, it’s essential to understand what dosage is appropriate for your needs. This will depend on factors such as age, weight, medical history, and any medications you’re currently taking. Consulting a healthcare provider who specializes in cannabinoid therapy can help determine the appropriate dosage for you.
What is the appropriate dosage of cannabinoids for medical use?
To figure out the optimal dosage of cannabinoids for your medical needs, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare provider who specializes in cannabinoid therapy. Dosing guidelines for cannabinoids are still being developed as research on their effects and benefits continues. However, clinical trials have shown that dosages can vary widely depending on individual factors such as age, weight, metabolism, and the specific condition being treated.
Administration methods also play a significant role in determining the appropriate dosage of cannabinoids. The process of consumption affects how quickly the effects take hold and how long they last. For instance, smoking or vaping cannabis produces quicker effects that may not last as long as edibles, which can take longer to feel but offer longer-lasting relief.
Patient education is therefore essential to ensure proper dosing and administration methods are used for maximum therapeutic benefit. With the help of your healthcare provider, you can determine an appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and circumstances.
In the next section, we’ll explore how different methods of consumption affect the effects of cannabinoids so you can make informed decisions about which administration method is right for you.
How do different methods of consumption (such as smoking, vaping, or edibles) affect the effects of cannabinoids?
You’re in for a wild ride when it comes to exploring the different methods of consuming cannabinoids. Smoking and vaping are popular options that provide immediate effects, but smoking can be harsh on your lungs and may cause coughing or other respiratory issues. Vaping, on the other hand, is considered safer than smoking and allows you to control your dosage more easily. Extream caution must be used to make sure you are not vaping synthetic cannabinoids like Delta-8.
Synthetic Cannabinoids: Dangers, Deaths, and Negative Research
Edibles and tinctures offer delayed effects that last longer than inhalation methods. Edibles take longer to kick in because they have to pass through your digestive system before entering your bloodstream. Tinctures are absorbed sublingually (under the tongue) and enter your bloodstream faster than edibles but slower than inhalation methods.
When consuming edibles or tinctures, dosing considerations are crucial as it can be difficult to determine how much THC or CBD you’re actually ingesting. Inhalation methods like smoking and vaping offer immediate effects while topical applications provide localized relief without affecting the rest of your body. However, dosing considerations apply here as well since applying too much topical cream or oil could lead to unwanted side effects.
Understanding how different consumption methods affect the effects of cannabinoids is vital in determining which method works best for you. Now let’s explore potential risks or concerns with using cannabinoids during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
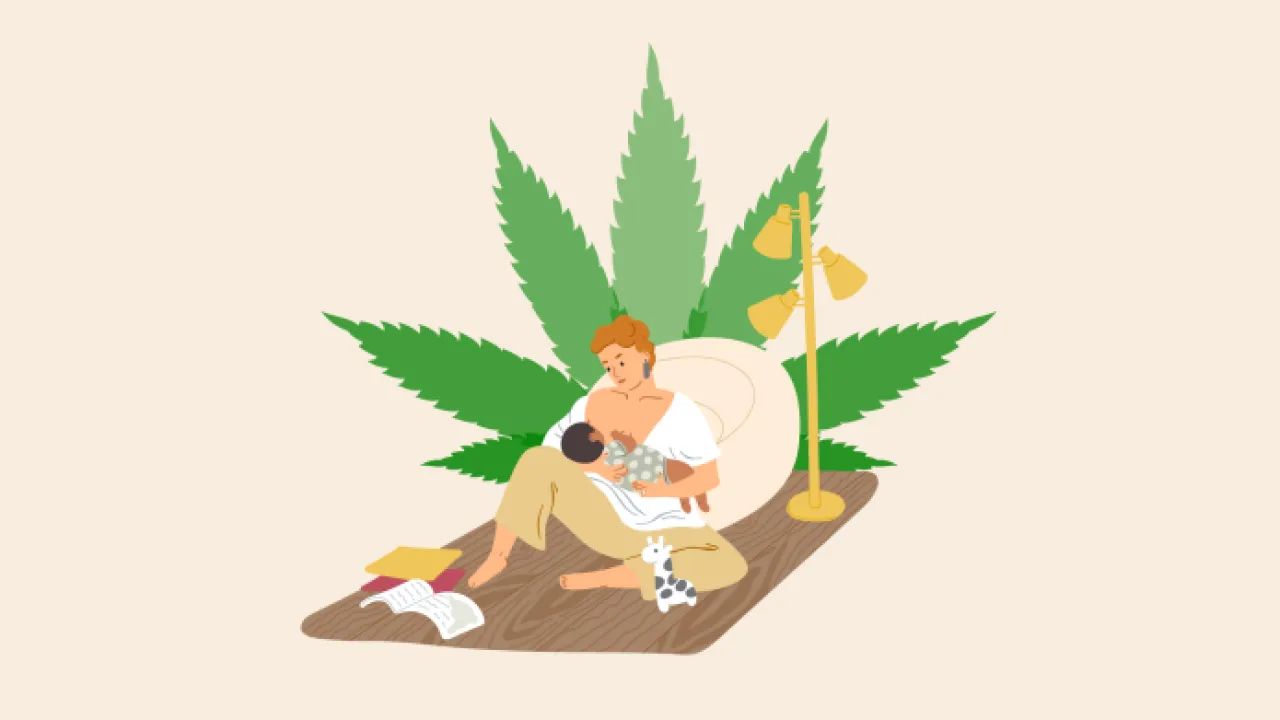
Are there any potential risks or concerns with using cannabinoids during pregnancy or while breastfeeding?
If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s important to know that using cannabis products could potentially harm your baby. While research on the effects of cannabinoids during pregnancy and breastfeeding is limited, studies suggest that THC exposure may negatively impact fetal development and lead to low birth weight. Additionally, THC can be passed through breast milk and may affect a nursing infant’s brain development.
Potential Risks: – Using cannabis during pregnancy may increase the risk of preterm labor – THC exposure during infancy has been linked to developmental delays – Breastfeeding mothers who use cannabis products may pass THC onto their babies through breast milk
Given the potential risks associated with using cannabinoids while pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s recommended that women avoid cannabis products altogether. If you’re considering using cannabinoids for medical purposes, it’s important to seek medical advice from a healthcare provider first.
As research on the effects of cannabinoids continues to evolve, it’s crucial for individuals to stay informed about potential risks and concerns related to their use.
In the next section, we’ll explore what current research is being conducted on cannabinoids and their potential medical uses.

What research is currently being conducted on cannabinoids and their potential medical uses?
Ongoing research is delving into the potential therapeutic properties of different cannabinoids and how they may be used to treat a variety of health conditions. Current research on cannabinoids focuses on their medical applications, including cannabinoid therapy for chronic pain, inflammation, epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and other disorders.
Clinical trials are underway to study the efficacy and safety of various cannabinoids in treating specific conditions. Pharmacological studies have shown that CBD has anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety effects without causing psychoactive effects. THC has been studied extensively for its pain-relieving properties but can also cause adverse side effects such as paranoia and memory impairment. Other lesser-known cannabinoids such as CBC, CBG, CBN, THCV, CBDA have also been studied for their unique therapeutic properties.
Despite ongoing research showing promising results in the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes, there are still legal barriers to obtaining them due to their classification as a Schedule I drug by the US federal government. However, more states are legalizing medical and/or recreational use of cannabis products containing certain levels of THC or CBD.
As research continues to uncover more about these compounds’ potential health benefits and risks in different populations with varying health conditions, regulating their production and distribution will become increasingly essential to ensure safe access for those who could benefit from cannabinoid therapy.
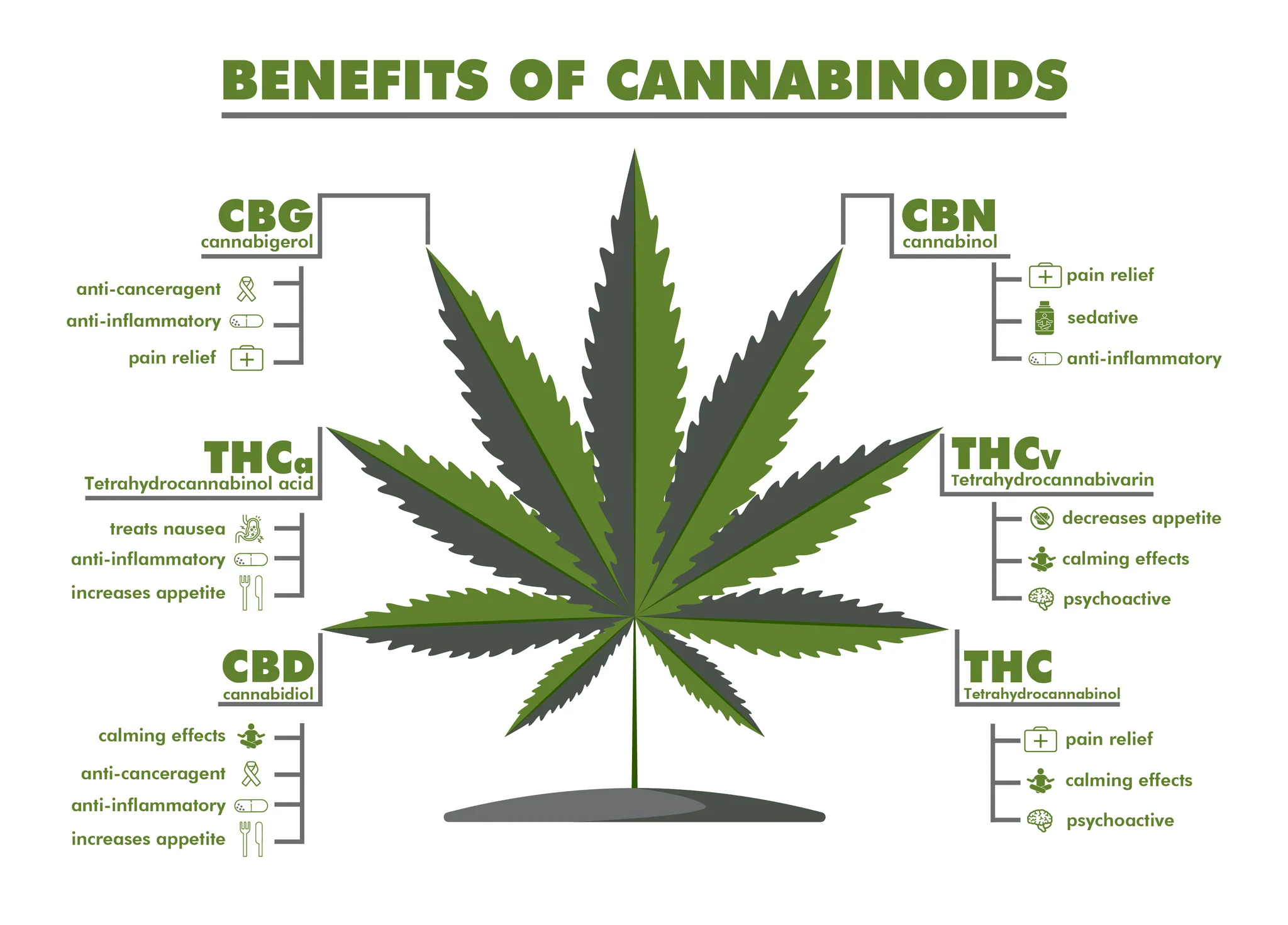
The Benefits of Cannabinoids
CBD is one of over 100 known cannabinoids. CBD and THC are the two most researched, but there are many other cannabinoids that have potential health benefits, including CBDV, CBN, CBG, CBC and THCA. Cannabinoids interact with receptors in our body called the endocannabinoid system. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2. This system helps regulate many important functions in our body such as mood, appetite and pain sensation. The system includes two types of neurotransmitters: endogenous (made by your brain) and exogenous (made by plants).What are cannabinoids?: What are cannabinoids? Cannabinoids are compounds that can bind to cannabinoid receptors found in the body. They produce their effects primarily by binding themselves to these proteins and thereby influencing things like cellular communication, emotional state, sleep patterns and even memory formation. What does the endocannabinoid system do? The endocannabinoid system interacts with nerve cells in your brain (neurons), helping control how you perceive sensations like pain, heat, or pleasure.

The difference between THC and CBD
A cannabinoid is a compound found in cannabis plants. To date, over 100 different cannabinoids have been identified, but THC and CBD are the two that capture most of the attention. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the best-known compounds, and it’s responsible for causing marijuana’s psychoactive effects. Cannabidiol (CBD) is another common component of cannabis; this non-psychoactive compound has been shown to reduce pain, inflammation, swelling, and more. Another significant difference between these two compounds is their chemical structure. THC contains three rings with an amine group attached to them at positions 2, 6, and 11 on the pentyl chain. CBD also includes three rounds, but they have a propyl chain instead of a pentyl chain with no amine group on position 3. These differences mean that they interact with each other differently when ingested or smoked – meaning you can still get high even if you consume CBD. Also noteworthy is that while research suggests many potential benefits of CBD use (like managing nausea), THC has only been proven beneficial with chemotherapy treatment because its toxic properties can be used against cancer cells while sparing healthy cells around them from damage.
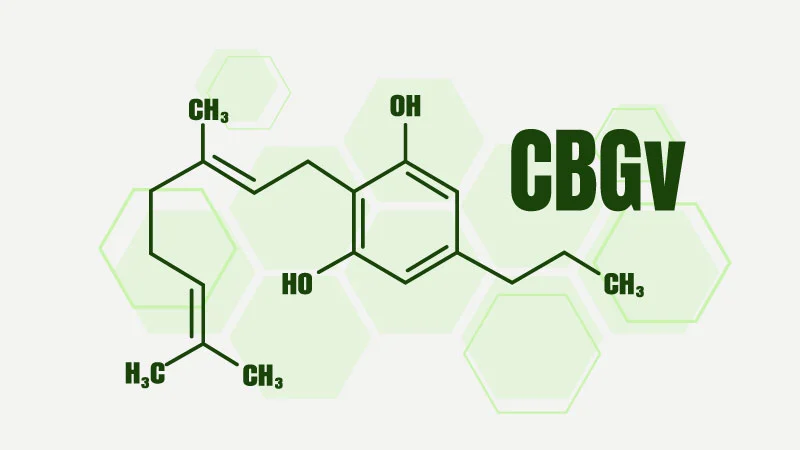
The difference between CBC and CBGV
CBC is a cannabinoid that has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, while CBGV is a cannabinoid that has been shown in preliminary research to offer neuroprotection. The two compounds also differ slightly in their molecular composition. Despite the differences, both CBC and CBGV are not as prevalent in cannabis plants as THC and CBD. However, CBC can be found in some European hemp varieties, and CBGV can be found in some strains of cannabis from South Africa.

What’s the difference between CBG and THCA?
Cannabis contains many forms of the molecule known as tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA). When this molecule is heated or cured, it becomes decarboxylated and converts into another molecule called Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), which then binds to CB1 receptors in the central nervous system. Thus, what we know as raw marijuana often doesn’t contain any detectable amounts of psychoactive chemicals like Δ9-THC. Instead, it’s converted into activated marijuana when smoked or vaporized for medicinal purposes.

The difference between CBDV and CBGV
CBCV is the chemical name for cannabichromevarin, reclassified as CBDV in 2010. One of the primary differences between these two compounds is that CBCV has a higher boiling point (around 212°F or 100°C) than CBDV (around 185°F or 85°C). Cannabichromevarin also seems more potent than cannabidivarin, with an estimated potency of 1.5%.
What are synthetic cannabinoids?
The dangers of synthetic cannabinoids are real, as evidenced by many reports of deaths and negative research findings. Synthetic cannabinoids arartificialde chemicals sprayed onto plant material or smoked to create a feeling similar to smoking marijuana. While the effects may be similar, the ingredients in synthetic cannabinoids are much more potent and have been linked to an increase in emergency room visits, serious health issues, and even death. See more about synthetic cannabinoids here.
Conclusion
Now that you understand the effects, benefits, risks, and legal status of cannabinoids for medical use, it’s important to remember that more research is needed in this field. However, CBD has gained popularity due to its potential health benefits and has been used to treat various ailments and diseases.
According to a recent survey conducted by Consumer Reports, 64% of Americans are in favor of legalizing marijuana for medical purposes. This shows a growing acceptance and interest in using cannabinoids for medical use.
It’s important to purchase CBD products from reputable companies and consult a healthcare provider before taking them. With further research and regulation, cannabinoids may become an even more effective treatment option for various health conditions.

Cannabinoid Acids
Cannabinoid acids, more commonly referred to as just cannabinoids, are chemical compounds that act as natural mood stabilizers. The two most abundant cannabinoids found in cannabis are tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). The process of conversion from THCA to THC is called decarboxylation; this process can be done through exposure to heat, light, or by leaving cannabis flowers out for a period of time. When heated, the THCA converts into its acidic form, CBGA. CBDVA (Cannabidivarinic acid) does not change when exposed to heat or light. CBGVA (Cannabigerovarinic acid), which is synthesized from THCVA (Tetrahydrocanabivarinic acid), converts into CBGVB if exposed to either heat or UV rays. CBCVA (Cannabichromevarinic acid) also does not change when heated.
CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid)
Cannabidiolic acid is an interesting cannabinoid because it’s a precursor to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), one of the most well-known cannabinoids. When cannabidiolic acid is heated, it converts into THC. However, when consumed as an isolated compound, CBDA doesn’t create psychoactive effects like THC does. In fact, the reverse may be true; consuming high doses of CBDA has been shown to decrease anxiety by activating GABA receptors. it can help reduce pain or treat neurological disorders such as epilepsy.
CBDA is known to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as potential anxiolytic and analgesic effects. Studies have also shown that CBDA can help to reduce nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy patients, as well as reduce seizures in patients with epilepsy.
The medicinal properties of CBDA make it an important component of CBD oil, as it helps to create an entourage effect when combined with other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC. By combining multiple cannabinoids, users are able to experience more balanced and therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, CBDA is an important cannabinoid found in CBD oil that offers many potential health benefits. By combining CBDA with other cannabinoids, users may be able to achieve a more therapeutic experience with their CBD oil.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
When talking about the different cannabinoids found in cannabis, one of the most discussed is cannabidiol, commonly referred to as CBD. What is CBD? It is a cannabinoid that has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its wide range of potential health benefits. Research has shown that it can help reduce inflammation, anxiety, depression, and even help fight cancer. It has also been linked to aiding in sleep, memory, and pain relief. CBD can be ingested in many different forms such as tinctures, edibles, topicals, and even vaping. However, the effects will vary depending on which form it was taken in. Tinctures are applied under the tongue or mixed with food and are absorbed more slowly than other methods but offer prolonged relief. Edibles take longer to absorb than tinctures but have strong effects when they do.Read more about CBD here.
Cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA)
Cannabidivarinic acid, or CBDVA, is an exciting cannabinoid found in hemp-derived CBD oil. It is one of the lesser-known cannabinoids and is becoming increasingly popular for its potential medical benefits.
CBDVA has the same chemical structure as cannabidivarin (CBDV), but with an additional carboxylic acid group, which has been shown to enhance its potential therapeutic effects. Unlike some other cannabinoids, CBDVA does not produce a high feeling.
Studies suggest that CBDVA may have some beneficial effects on various conditions, including inflammation, anxiety, and epilepsy. In addition, research suggests that CBDVA may be more effective than CBD alone in treating some conditions. For example, a study published in the journal Neurotherapeutics found that CBDVA was more effective than CBD in treating seizures in mice.
It is important to note that research into the potential benefits of CBDVA is still in its early stages, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential medical benefits. However, it is clear that CBDVA could be an exciting addition to the world of cannabinoids and offer new therapeutic possibilities.
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
CBDV has been found to possess anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic properties, as well as being effective in treating certain neurological conditions. Studies have also demonstrated its ability to protect against oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases. As such, CBDV has become a popular option for those seeking relief from various physical and mental ailments.
In addition to its therapeutic benefits, CBDV has also been studied for its potential use in treating certain forms of epilepsy. A recent study showed that CBDV was effective in reducing seizures in mice, suggesting that it may be useful in treating certain types of epileptic disorders. While more research is needed in this area, these findings are promising.
CBDV can be found in many different forms, including tinctures, capsules, and edibles. It is important to note that CBDV can interact with other medications and supplements, so it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking it. Additionally, it is important to purchase CBD products from reputable companies that test their products for quality and safety.
Cannabichromenenic acid (CBCA)
CBCA (Cannabichromenenic acid): Another important cannabinoid that makes cannabis more therapeutic than recreational is cannabichromene or CBCA for short. It’s not thought to be active at binding with either the CB1 or CB2 receptors like CBD, but instead activates another receptor called GPR18 which suppresses inflammation responses within the brain and body while triggering a sedative effect.
Cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA)
Cannabichromevarinic acid is one of at least 113 cannabinoids that has been isolated from cannabis plants. It is a minor constituent of hemp varieties grown primarily to produce fiber. This means it’s not as common as CBD, THC, or CBN. The most potent derivative of CBVA is CBCV (Cannabichromenic acid). So far, there haven’t been any studies done on its medical efficacy. But because it is an analogue of cannabichromene, it may have similar properties. In a study published by the International Journal of Legal Medicine researchers found that when rats were given doses equivalent to 1/10th and 1/5th human dosage, they did not exhibit typical side effects seen with other non-psychoactive cannabinoids like cannabidiol.
CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid)
CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid)
CBGA is an acid that is found in the cannabis plant. It is the precursor to THC, CBN, and CBD. It can be used to decarboxylate other cannabinoids such as THCA into THC, or CBDA into CBD. The endocannabinoid system is responsible for regulating many physiological processes including appetite, immune response, moods/emotions, bone growth and repair as well as pain management. CBGA inhibits tumor cell proliferation and has been shown to inhibit a gene associated with aggressive breast cancer cells. The biosynthetic pathway of CBGA begins with geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) which then produces cannabigerol (CBG). GPP is converted by cyclization to form either farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) or geranyl diphosphate (GDP). GDP then undergoes reduction reactions to form 2-trans-delta8-cis-tetrahydrocannabinol. FPP also undergoes reduction reactions to produce 2-cis-delta8-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol, but it does not give rise to tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid from the intermediate δ8 -THCV.
CBG (Cannabigerolic)
CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, meaning it doesn’t produce the same psychoactive effects as THC. CBG has been shown to have many therapeutic potentials and can be used in the treatment of inflammation, pain, and even cancer. In fact, CBG is thought to work synergistically with other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC. Some research suggests that CBG may also be able to block some of the negative side effects caused by THC such as anxiety or paranoia.CBG has yet to be extensively researched for its medicinal properties but there are promising signs that this cannabinoid could hold a wealth of information about how cannabis can help our bodies heal.Learn more about CBG here! What are cannabinoids? Cannabinoids (CBD, THC, etc) are chemical compounds that come from the cannabis plant. Different cannabinoids interact with receptors in your brain and body differently to produce different effects on your health – this is what’s referred to as their mechanism of action.
Cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA)
Cannabigerovarinic acid, or CBGVA, is one of many cannabinoids found in cannabis. CBGVA is a product of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) and can be converted to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) via decarboxylation. CBGVA has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties with moderate efficacy as an antibiotic against certain species of bacteria. It also possesses antiviral activity and is used in vitro for treating fungal infections. CBGVAs potential to inhibit cancer cell growth has been investigated but was not conclusive.
Cannabicyclol (CBL)
Two other lesser-known cannabinoids present in CBD oil are cannabicyclol (CBL) and cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA). These two compounds work together to produce unique effects in the body. CBL has been shown to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. CBLA can act as an agonist at CB1 receptors, which can be beneficial for mood disorders. Together, CBL and CBLA are a powerful combination for those seeking relief from inflammation and pain.
Cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA)
CBD oil has become a popular health supplement due to its potential therapeutic benefits. It is a natural extract derived from the Cannabis plant, and it contains cannabidiol (CBD) as one of its main components. Alongside CBD, there are several other cannabinoids found in CBD oil, such as cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA).
CBLA is thought to work synergistically with other compounds found in CBD oil, such as CBD and CBDA, to create an even more powerful therapeutic effect. For this reason, many people use CBD oil for their health concerns in order to take advantage of the combined benefits of all of these compounds.
If you’re looking to reap the therapeutic benefits of CBD oil, make sure to check if it contains CBLA. It could be the key to unlocking even more of CBD oil’s potential benefits!
Cannabicyclovarin (CBLV)
CBD oil has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its many potential health benefits. One of the compounds found in CBD oil is cannabicyclovarin (CBLV). CBLV is an analog of the cannabinoid THC, and has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and anti-nausea properties.
CBLV interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system by binding to the CB1 receptor in the brain. This interaction can help reduce inflammation, anxiety, and nausea. In addition, CBLV may also be helpful for treating seizures, as studies have shown it to be effective in reducing the severity and duration of seizures in mice.
Overall, CBLV is an important compound to be aware of when considering CBD oil as a natural treatment for various health issues. While more research is needed to fully understand its effects and benefits, current research suggests that CBLV could be an effective option for those looking for natural remedies to treat various health conditions
Cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA)
CBDVA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found naturally in cannabis. Unlike THC, CBDVA does not produce any kind of psychoactive effects, but it can still be used to create them by mixing it with other cannabinoids like THC.There is not much research on CBDVA specifically, but some studies have been done on rats. These studies found that CBDVA helped to reduce nausea and vomiting without any unwanted side effects. It may also help reduce anxiety and depression, as well as inflammation. The amount needed for these effects is not known at this time, so more research needs to be done before we know if this is true. However, one study suggested that CBDVA might be an effective treatment for certain symptoms of fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis. Studies have also shown it to act as an antioxidant which can protect against cellular damage from free radicals.
Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA)
Unlike most cannabinoids, THCA is not psychoactive. This cannabinoid is also known as a precursor because it can be converted to THC. Other cannabinoids that can be converted to other cannabinoids include CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid) to CBGVA (Cannabigerovarinic acid), CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid) to CBDVA (Cannabidivarinic acid), CBCA (Cannabichromenenic acid) to CBCVA (Cannabichromevarinic acid).There are more than 100 different types of cannabinoids found in cannabis, but only some of them provide a wide range of health benefits. For example, cannabidiol is widely used for its ability to counteract seizure disorders and for its anxiolytic effects. In contrast, tetrahydrocannabinol or THC is highly psychoactive due to its ability to bind with cannabinoid receptors in your brain allowing you to feel high . The other four best-known cannabinoids are cannabigerol or CBG , cannabichromene or CBC , cannabigerovarinic acid or CBGV and cannabinolic acid or CBNA . All these compounds have medicinal properties.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
What is Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)? THC is the main psychoactive component of cannabis and is responsible for its characteristic high. It works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and produces a range of effects, such as changes in mood, appetite, and perception. THC can also cause increased heart rate, red eyes, dry mouth, and other physical side effects. Research has shown that THC may have medicinal benefits as well, such as reducing pain and inflammation.
Tetrahydrocanabivarinic acid (THCVA)
THCVA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is an analogue of THC. It was first isolated by Shimon Ben-Shabat, Yechiel Gaoni, and Raphael Mechoulam in 1998. It has a melting point at 186 degrees Celsius, which is lower than THC’s melting point of 188 degrees Celsius. This may make it more difficult to extract from cannabis. Its boiling point is 220 degrees Celsius, which makes it volatile when heated to high temperatures like THC. When heated up with cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), you can get tetrahydrocannabivarin carboxylic acid (THCVC) instead of THCVA.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that interact with receptors throughout the body to produce pharmacological effects. Tetrahydrocannabinol is one of many cannabinoids found in cannabis. THCV has been shown to suppress appetite and may be helpful for people trying to lose weight. CBD has been shown to reduce or eliminate seizures due to epilepsy and provide relief for those suffering from chronic pain. CBDA may have anti-inflammatory properties; however, it needs more research before any claims can be made about its medicinal benefits.
CBN is non-psychoactive and is mainly used for its ability to help treat insomnia. Another cannabinoid, CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid), is non-psychoactive but artificially helps regulate physiological functions, including sleep cycles. Another important cannabinoid is CBCA (Cannabichromenenic acid) which has strong anti-inflammatory properties and may have some antibiotic qualities. It’s worth noting that these findings are still preliminary and require further research.
It is essential that if you are going to try a Full Spectrum hemp CBD Oil that contains a rich, robust blend of cannabinoids. The Genesis Blend Hemp Extract CBD Oil has more cannabinoids and terpenoids than any other brand.